We present LiteralKG, a novel GNN model for learning literal-aware representations of medical knowledge graphs, which can integrate different types of literal information and graph structural features into unified vector representations. LiteralKG is developed by NS Lab, CUK, based on pure PyTorch backend.
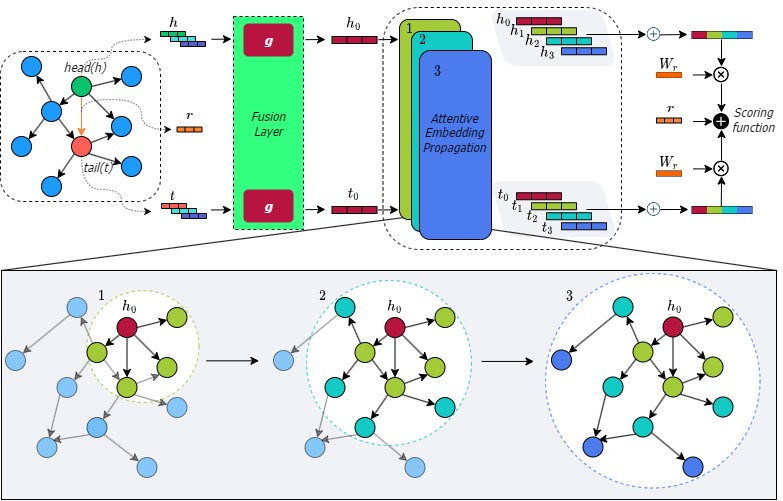
The overall architecture of LiteralKG.
Over the past few years, Knowledge Graph (KG) embedding has been used to benefit the diagnosis of animal diseases by analyzing electronic medical records (EMRs), such as notes and veterinary records. However, learning representations to capture entities and relations with literal information in KGs is challenging as the KGs show heterogeneous properties and various types of literal information. Meanwhile, the existing methods mostly aim to preserve graph structures surrounding target nodes without considering different types of literals, which could also carry significant information. We propose LiteralKG, a knowledge graph embedding model for efficiently diagnosing animal diseases, which could learn various types of literal information and graph structure and fuse them into unified representations. Specifically, we construct a knowledge graph that is built from EMRs along with literal information collected from various animal hospitals. We then fuse different types of entities and node feature information into unified vector representations through gate networks. Finally, we propose a self-supervised learning task to learn graph structure in pretext tasks and then towards various downstream tasks. Experimental results on link prediction tasks demonstrate that our model outperforms the baselines that consist of state-of-the-art models.
A short description of LiteralKG:
- We construct a medical knowledge graph that comprises 595,172 entities and 16 relation types from various EMRs.
- LiteralKG could learn different types of literal information and graph structure and then fuse them into unified representations.
- LiteralKG, a self-supervised learning framework for Knowledge Graph, that could learn the graph structure from pretext tasks to generate representations, and then the pre-trained model is used for downstream tasks to predict animal diseases.
- The experimental results on the KG with different types of GNN aggregators and residual connection and identity mapping show the superiority of LiteralKG over baselines.
The LiteralKG is available at:
Cite “LiteralKG” as:
Please cite our paper if you find LiteralKG useful in your work:
@Article{Hoang2023,
author = {Van Thuy Hoang and Thanh Sang Nguyen and Sangmyeong Lee and Jooho Lee and Luong Vuong Nguyen and O-Joun Lee},
title = {Companion Animal Disease Diagnostics Based on Literal-Aware Medical Knowledge Graph Representation Learning},
journal = {IEEE Access},
year = {2023},
volume = {11},
pages = {114238--114249},
month = oct,
issn = {2169-3536},
doi = {10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3324046},
}
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()




